Using Change Data Capture with Google Cloud SQL for MySQL
Use DataCater for streaming change events from Google Cloud SQL for MySQL to your data sinks.
Use DataCater for streaming change events from Google Cloud SQL for MySQL to your data sinks.
In this article, we discuss how to use DataCater for capturing data change events from a Google Cloud SQL for MySQL instance and stream them to other systems in real-time.
Imagine a scenario where we have several microservices in production and we need to track and monitor the health status of each microservice.
Health information are managed in a MySQL table:
+------------+-----------------------+-------------+---------------+ | service_id | service_name | service_env | access_status | +------------+-----------------------+-------------+---------------+ | 1 | auth_service | prod | Yes | | 2 | mail_service | prod | Yes | | 3 | flag_service | prod | Yes | | 4 | redis_service | prod | Yes | | 5 | postgres_service | prod | Yes | | 6 | broker_service | prod | Yes | | 7 | monitor_service | prod | Yes | | 8 | AI_service | prod | Yes | | 9 | rabbitmq_service | prod | Yes | | 10 | kafka_service | prod | Yes | | 11 | pulumi_service | prod | Yes | | 12 | log_service | prod | Yes | | 13 | elasticsearch_service | prod | Yes | | 14 | grunt_service | prod | Yes | +------------+-----------------------+-------------+---------------+
Anytime a service is not reachable by other services, the column access_status is updated and set to No.
We can use change data capture to monitor the health status of the microservices in real-time, allowing us to take immediate action. Technically, DataCater extracts change events from the Binlog of MySQL using Debezium.
In the following article, we assume that you have an existing instance up and running. If not, please create a new Google Cloud SQL for MySQL instance.
By default, external networks (services outside the jurisdiction of Google Cloud Platform) can’t access GCP services. So we need to grant DataCater appropriate permission to access our Cloud SQL for MySQL instance.
Go to the instance in your cloud console and click on Connections.
Add a new network and provide DataCater Cloud as the name and
DataCater’s public IP address 20.79.84.135 for the network:
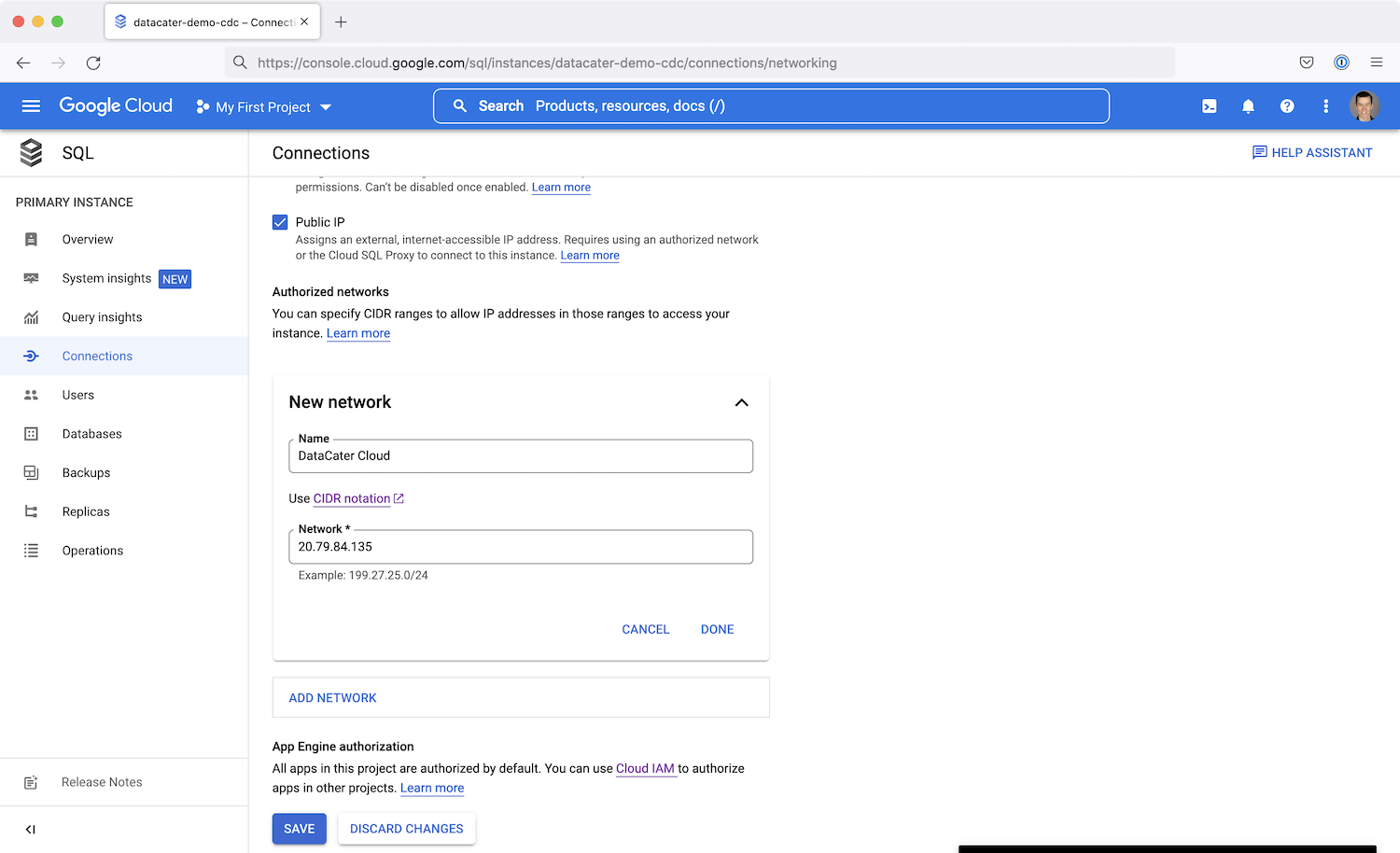
Save the configuration by clicking Done and Save.
Next, create a separate MySQL user for DataCater.
Go to Users. Click Add user account and add a new user for DataCater:
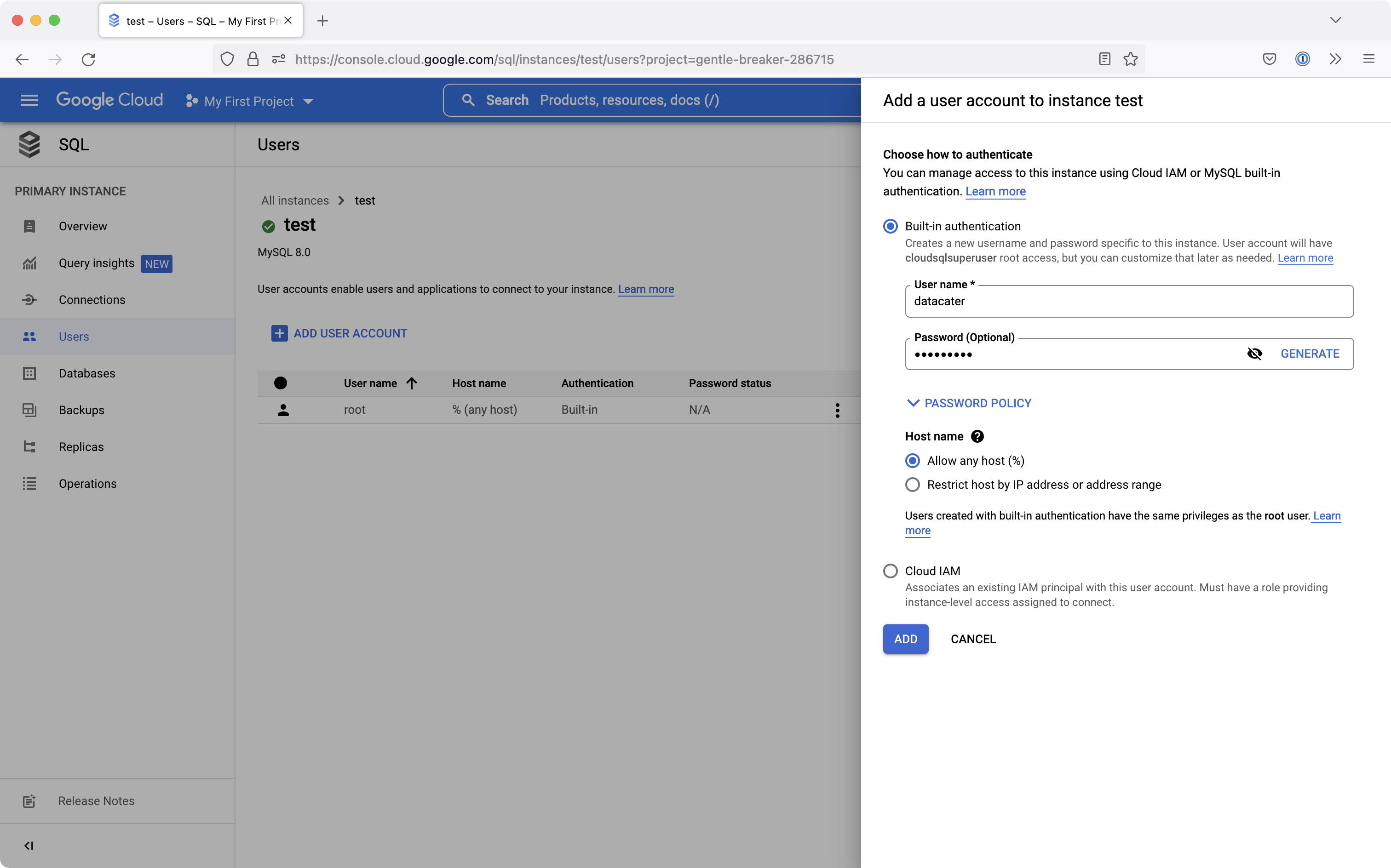
Provide a username and password and click Add.
Make sure that the created user has the permissions needed for accessing the binlog of MySQL.
Connect to the MySQL instance using the command line tool mysql
and execute the following action (assuming that your user is called
datacater):
GRANT SELECT, RELOAD, SHOW DATABASES, REPLICATION SLAVE, REPLICATION CLIENT ON *.* TO datacater;
You might also consider working with user groups instead of single users. In this case, you can assign the needed permissions to the group.
Sign up for a free DataCater trial unless you already have an account.
After signing in to DataCater Cloud, click on Data Sources at the top and choose MySQL as the data source type.
Next, provide the connection credentials of your Cloud SQL for MySQL instance:
Then press on the test connection button to test the connection to Cloud SQL MySQL.
In the case that the connection to Cloud SQL for MySQL fails, (1) check if the Cloud SQL MySQL instance is still running, (2) verify that you have provided correct credentials, and (3) check if DataCater has network access to your Cloud SQL for MySQL instance.
Finally, click on Create data source to save everything.
Navigate to Data sinks and create a new data sink. You can choose from any of the supported data sink types, e.g., Google Cloud BigQuery, or REST/HTTP.
Next, create a new pipeline in DataCater that consumes the data source we created for Cloud SQL for MySQL and publishes data to your data sink.
If you want to process the change events from MySQL, you can define filters and transformations inside your pipeline.
Finally, create a deployment for your pipeline to start streaming change events from your Cloud SQL for MySQL instance to your data sink.
Keen to try it out? Sign up for our free trial and experience real-time data streaming in a matter of minutes.
Try change data capture with your Cloud SQL for MySQL instance, for free
Get started with our plug & play CDC connector for MySQL. Stream change events to your downstream applications in real-time.